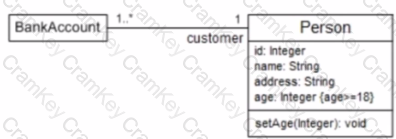
Explanation: In UML 2, a class diagram is used to depict the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, operations (or methods), and the relationships among the classes. The constraint{age >= 18}in thePersonclass diagram indicates a condition that must hold true for the instances of thePersonclass whenever they are used in the context of aBankAccount. This constraint is an invariant of thePersonclass that specifies the rule for the attributeage.
Now, let's consider the provided options and explain why option B is correct:
A. The preferred age to open a bank account is 18 years old or older – This statement is incorrect because the diagram does not indicate a preference; it indicates a constraint or a rule.
B. Only customers who are 18 years old or older can open a bank account – This is the correct statement. The{age >= 18}constraint next to theageattribute of thePersonclass signifies that any instance ofPersonassociated with aBankAccountmust be at least 18 years old. SincePersonis connected toBankAccountwith the role namecustomer, this implies that only persons who are at least 18 can be customers of a bank account.
C. The age condition should only hold when the setAge(Integer) function is called – This statement is incorrect because the constraint{age >= 18}is not a condition that applies only when thesetAgeoperation is invoked. Instead, it is a class invariant that must always hold true for any instance ofPerson.
D. An object of Customer with age set to 18 or greater will raise an exception – This is incorrect because the UML diagram specifies a constraint, not an exception condition. The constraint ensures validity, not the raising of an exception.
The answer is verified according to the UML 2 Foundation documents, such as the UML 2.5 specification, where class diagrams and constraints are defined. The specification states that constraints are semantic conditions or restrictions expressed in natural language text or in a machine-readable language that must hold true for the system being modeled (UML 2.5 specification, section 7.9).