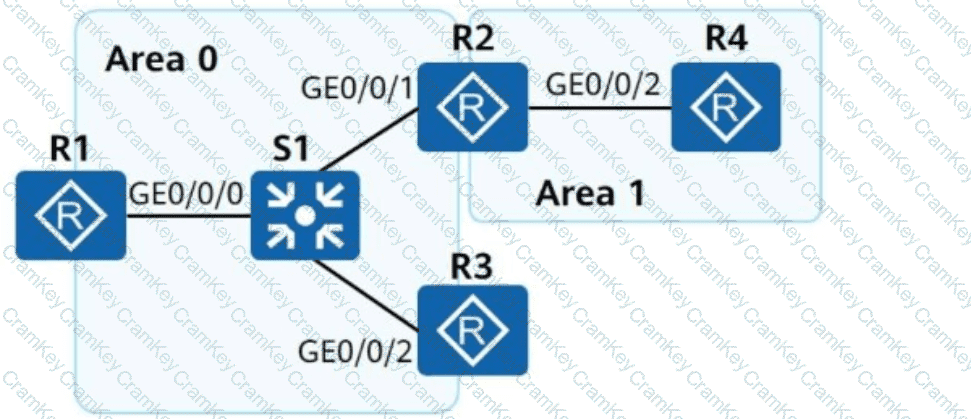
Let's dissect each option based on OSPFv3 LSA behavior from Huawei HCIE Datacom documentation.
✅ Option A: Correct
OSPFv3 uses Router LSAs (Type 1) to describe the local interfaces, links, and neighbors.
R1, as part of Area 0, will generate Router-LSAs and receive Router-LSAs from neighbors in the same area (R2 and R3 via switch S1).
Huawei Datacom Reference:
"Each OSPFv3 router originates a Type 1 Router LSA for each area it belongs to."
(Source: HCIE-Datacom Study Guide v3.0 - OSPFv3 Fundamentals)
❌ Option B: Incorrect (Correct Answer)
Link-LSAs (Type 8) are not sent between routers. They are only generated for each link on which the router has at least one neighbor. These LSAs are only flooded on the local link.
R1 cannot receive two Link-LSAs from R2 about both links. It can only receive the Link-LSA that R2 generates for the shared link with R1. The other link (e.g., to R4 in Area 1) is irrelevant to R1.
Huawei Datacom Reference:
"A Link LSA is generated by a router for each attached link and is sent only to the routers on the same link."
(Source: HCIE-Datacom Study Guide v3.0 - OSPFv3 LSA Types)
✅ Option C: Correct
On broadcast links, DRs generate Type 2 Network LSAs.
If R3 is the DR on the shared segment (with R1), R1 will have the Network-LSA from R3 in its LSDB.
Huawei Datacom Reference:
"The DR on a broadcast network generates a Type 2 Network LSA to describe all routers on that link."
(Source: HCIE-Datacom Study Guide v3.0 - OSPFv3 LSDB Construction)
✅ Option D: Correct
R2 connects Area 0 and Area 1, hence it's an ABR.
ABRs generate Type 3 Inter-Area-Prefix LSAs to advertise IPv6 prefixes from one area to another.
R2 advertises Area 1 prefixes to Area 0 routers (R1 and R3).
Huawei Datacom Reference:
"Inter-Area-Prefix LSAs (Type 3) are generated by ABRs to advertise IPv6 prefixes from one area into another."
(Source: HCIE-Datacom Study Guide v3.0 - ABR Functionality in OSPFv3)