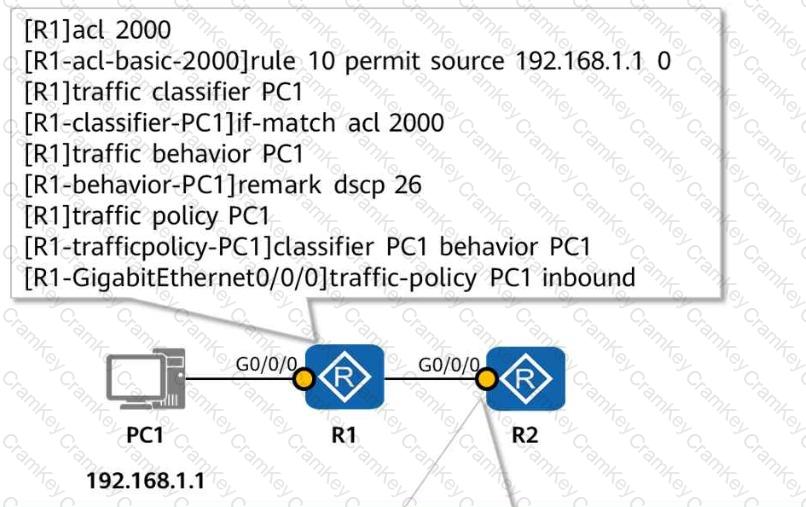
Understanding EVPN (Ethernet VPN) Label Allocation and ARP Handling
????What Happens in This Scenario?
1️⃣CE1 (192.168.1.1) sends an ARP request to discover the MAC address of CE2 (192.168.1.2).
2️⃣PE1 receives the ARP request and needs to forward it over the EVPN fabric.
3️⃣To send the broadcast ARP request across the EVPN network, PE1 forwards the packet to PE4 using BUM (Broadcast, Unknown unicast, and Multicast) forwarding.
4️⃣PE4, as the Designated Forwarder (DF), forwards the ARP request to CE2.
Role of Labels in EVPN VXLAN/MPLS Networks
????EVPN uses BGP to distribute MAC/IP reachability information using different route types.
✅EVPN Type 2 Route (MAC/IP Advertisement Route):
Used forMAC-to-IP address mappingannouncements.
Ensuresremote VTEPs (PE routers) learn MAC-to-IP bindingsdynamically.
✅EVPN Type 3 Route (Inclusive Multicast Route):
Used forBUM traffic (Broadcast, Unknown Unicast, Multicast).
Assigns a multicast label (e.g., 201) to be used for forwarding broadcast packets like ARP requests.
????In this case:
Thelabel 201is used forBUM traffic forwarding.
BUM traffic is handled using an EVPN Type 3 route.
Why is the Answer 3?
✅EVPN Type 3 routes carry labels for BUM traffic, which includes ARP requests.
✅Label 201 is used for multicast distribution, which is managed by Type 3 routes.
Real-World Application:
VXLAN Data Centers:UsesEVPN Type 3 routes to control BUM traffic efficiently.
Campus Networks:Preventsunnecessary flooding of ARP requests across VXLAN domains.
✅Reference:Huawei HCIE-Datacom Guide – EVPN BGP Route Types and Multicast Labeling